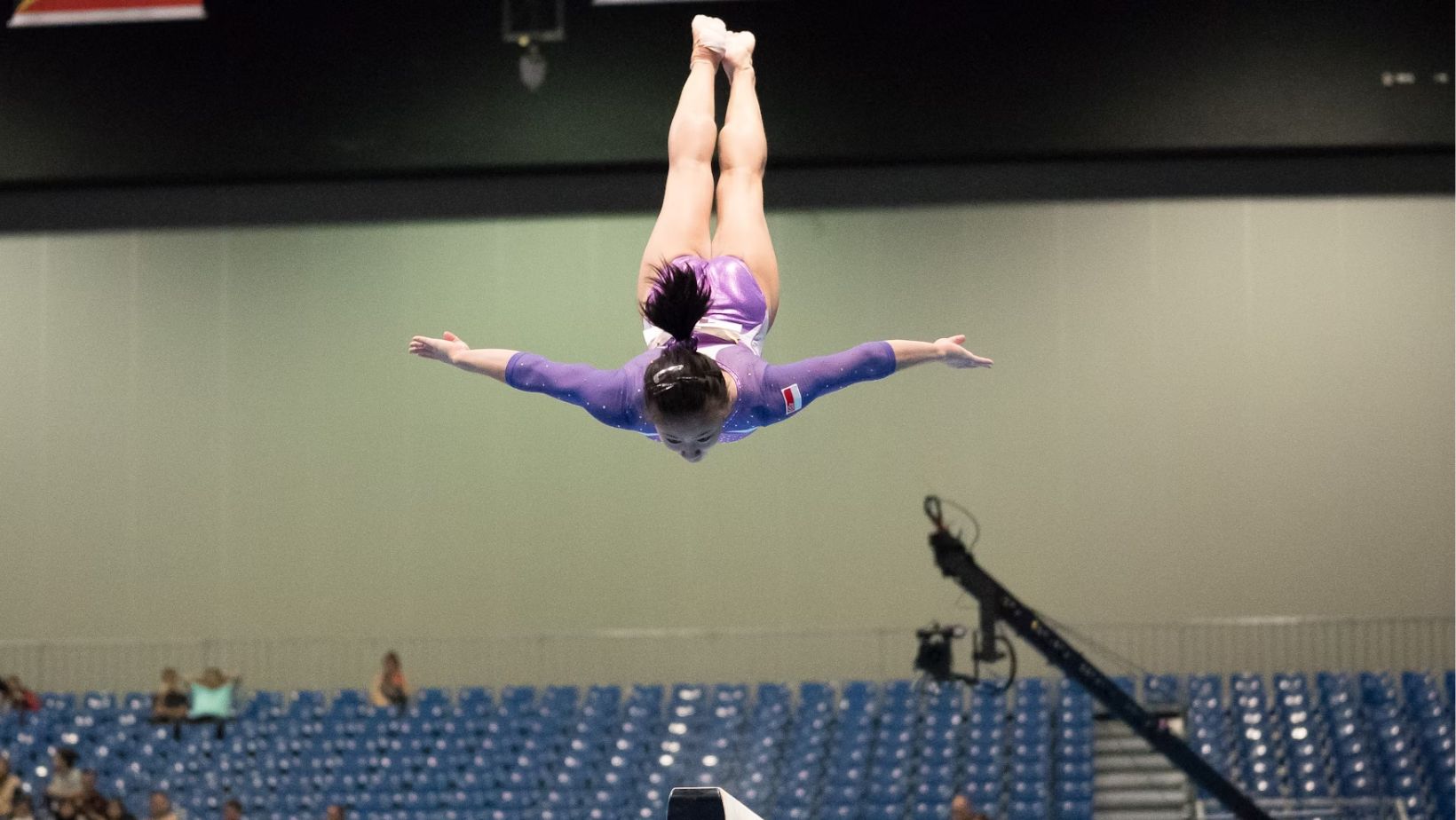
The Olympic Games showcase the pinnacle of human athletic performance. Competitors across various sports push the boundaries of physical and mental endurance, displaying fitness levels that inspire and amaze spectators worldwide. Understanding the fitness levels of these elite athletes offers valuable insights into the dedication, training, and discipline required to reach the top.
The Physical Demands of Different Sports
Every sport at the Olympics 2024 demands a unique combination of strength, speed, endurance, and flexibility. Athletes tailor their training to excel in their specific events, resulting in highly specialized fitness profiles.
Endurance Sports
Marathon runners, swimmers, and cyclists fall into the endurance category, requiring exceptional cardiovascular fitness. Their training involves long-duration exercises designed to enhance stamina and cardiovascular efficiency. Marathon runners often log over 100 miles a week, while swimmers might spend several hours daily in the pool, fine-tuning their technique and building endurance.
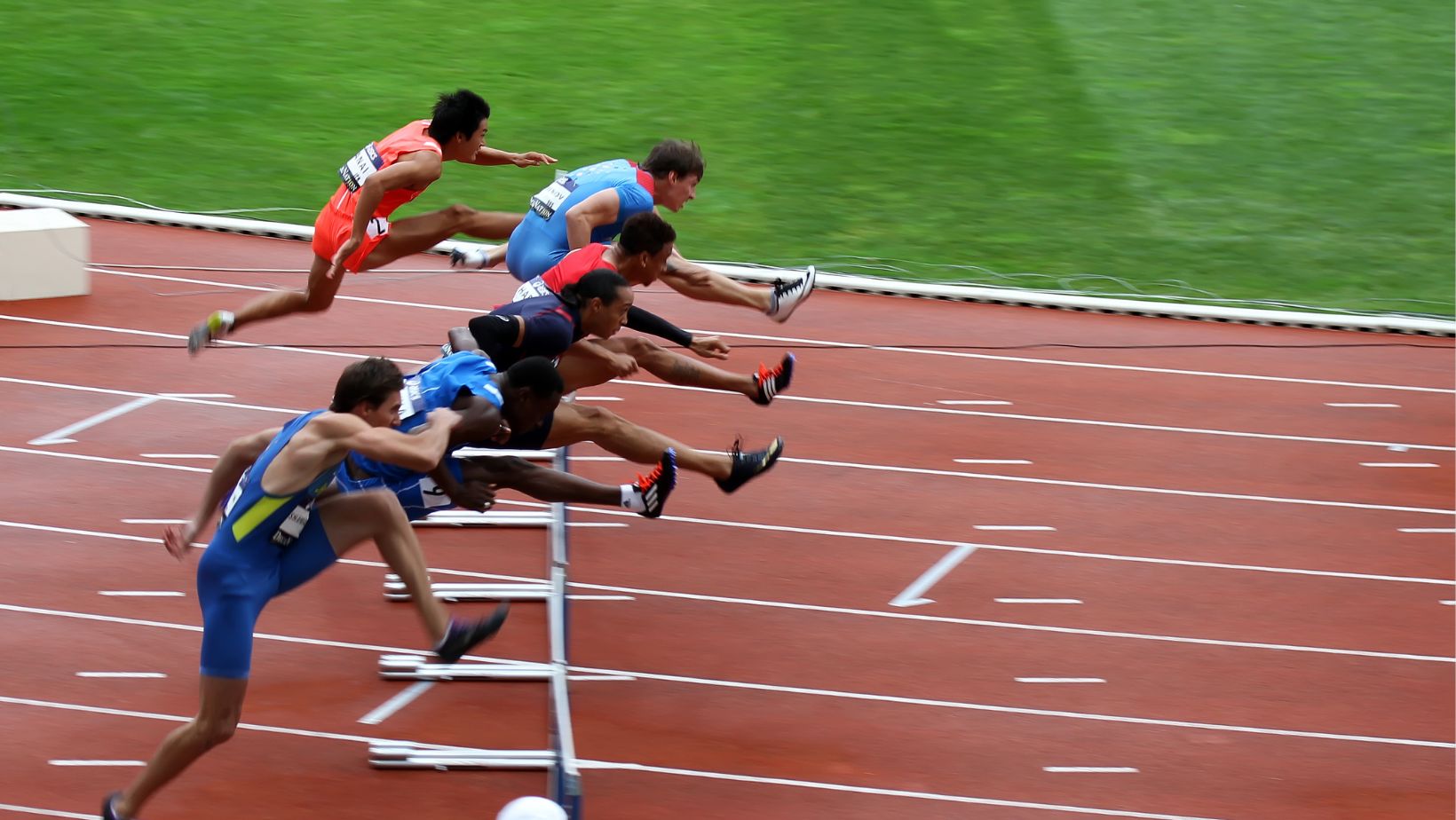
Power and Strength Sports
Weightlifters, sprinters, and shot putters rely heavily on explosive power and strength. These athletes focus on short, intense bursts of activity. Their training regimens include heavy lifting, plyometrics, and sprint drills. For instance, a sprinter might perform repeated 100-meter sprints with brief rest periods, while weightlifters engage in rigorous sessions lifting maximal weights to build muscle and power.
Skill and Precision Sports
Gymnasts, archers, and fencers prioritize skill, precision, and flexibility. These athletes train to develop fine motor skills, balance, and body control. Gymnasts, for instance, spend countless hours perfecting routines that require incredible strength and flexibility, while archers focus on steadying their hands and enhancing their focus to hit the target accurately.
The Role of Nutrition in Athletic Performance
Nutrition plays a critical role in an Olympic athlete’s training and performance. A balanced diet tailored to the specific needs of the sport is essential for optimal performance.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the primary fuel sources.

Endurance athletes need a high carbohydrate intake to sustain prolonged energy expenditure, while power athletes require more protein to repair and build muscle. A balanced diet ensures that all athletes maintain energy levels and recover effectively from intense training sessions.
Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals are equally vital. Athletes must ensure adequate intake of iron, calcium, and vitamin D to support oxygen transport, bone health, and muscle function. Supplements like multivitamins or greens powder supplements may be necessary to meet these demands, especially during intense training phases.
Mental Fitness: The Unsung Hero
Physical prowess alone does not define an Olympic athlete. Mental fitness is equally crucial, involving focus, resilience, and the ability to perform under pressure.
Psychological Training
Athletes often work with sports psychologists to develop mental toughness. Techniques such as visualization, mindfulness, and goal-setting help athletes stay focused and motivated. Visualization, for instance, allows athletes to mentally rehearse their performances, reducing anxiety and enhancing confidence.
Coping with Pressure
Competing on the world stage brings immense pressure. Successful athletes learn to cope with this through mental strategies and a strong support network.

They might practice deep breathing exercises, maintain a positive mindset, or rely on the encouragement of coaches and teammates to stay grounded.
The Recovery Process
Recovery is a vital component of an athlete’s fitness regime. It ensures they can continue training effectively and avoid injuries.
Active Recovery
Active recovery involves low-intensity exercises, such as light jogging or swimming, to promote blood flow and reduce muscle soreness. It helps athletes recover while still staying active.
Passive Recovery
Passive recovery includes rest, sleep, and therapeutic interventions like massage and physiotherapy. Adequate sleep is crucial, as it allows the body to repair and regenerate tissues. Many athletes also use ice baths, compression garments, and stretching routines to enhance recovery.
Conclusion
The fitness levels of Olympic athletes result from a combination of rigorous physical training, meticulous nutrition, mental resilience, and effective recovery strategies. These athletes dedicate their lives to perfecting their craft, demonstrating what the human body and mind can achieve. Their commitment to excellence sets a standard for aspiring athletes and inspires people worldwide to pursue their own fitness goals.
